Waterborne polyurethane (WPU) is an important polymer material, which can be used as coating material, adhesive, paint, foam and so on [1], [2]. With water as the solvent, WPU has the advantages of environmental protection and less pollution. With the limit of pollutant emission by the government, WPU have attracted more and more attention, and is expected to partially or completely replace the traditional solvent-based PU in the market. Generally, the main raw materials of WPU are isocyanates and polyols [3], and most of these major raw materials come from petroleum-based products, which are not renewable. With the exhaustion of petroleum products, people gradually began to look for alternatives to petroleum-based raw materials. Currently, only a few isocyanates are available and purchased, such as IPDI, HDI and TDI, but most polyols can be designed and replaced. Some renewable raw materials from nature, such as lignin, cellulose, starch, etc. were gradually used in the preparation process of polyurethane as polyols [4], [5].
Vegetable oil has become a good alternative to petroleum because of its advantages of easy availability, low cost, abundant yield, green and sustainable [6], [7], [8]. Some researchers have synthesized a series of bio-based WPU by vegetable oil-based polyols as raw materials, such as soybean oil, rapeseed oil, cottonseed oil and so on [9]. Natural castor oil (CO) is extracted from castor oil seeds, and it carries hydroxyl groups. Therefore, without modification, CO can be used as polyols to synthesize WPU. Castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane (CWPU), prepared from CO as raw polyols, has been widely studied for its advantages of green and environmental protection [10], [11], [12]. However, due to the limited hydroxyl group of CO molecule and the low activity of secondary hydroxyl group, the crosslinking degree of CWPU is low, which leads to its poor stability and restricts its wide use [13]. The thermal physical properties and mechanical properties of castor oil-based polyurethane can be improved by increasing crosslinking [14], [15]. Silane coupling agent is common crosslinking agent [16], [17], however, the low surface energy element Si from silane coupling agent leads to the phase separation phenomenon on the surface of coating [18], [19]. The vegetable oil-based crosslinkers are branched molecule with multiple reactive groups, which are synthesized from vegetable oil. Vegetable oil-based crosslinkers not only have good compatibility with bio-based coatings, but also are renewable and environmentally friendly. The introduction of vegetable oil-based crosslinkers into castor oil-based polyurethane is an effective modification method to avoid phase separation problems [20], [21].
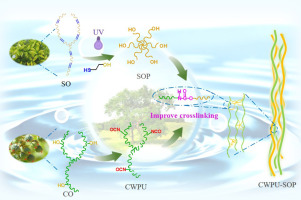
Sapium sebiferum oil (SO), refined from the sapium sebiferum tree, is a non-edible vegetable oil, which avoids the problem of competing with people’s food [22]. With high iodine value (up to 186.8 g), SO contains more than 90% unsaturated fatty acids, which makes it easy for abundant double bonds to be modified. And it was used in the production of biodiesel in the past, which also provides the basis for its use as a chemical raw material [23]. With high iodine value, the average number of double bonds per molecule of SO is 6.6, much higher than that of castor oil (3.0) and soybean oil (4.5) [24], so it can be converted into a crosslinking agent by hydroxylation modification of unsaturated double bonds. Natural SO modified by introducing hydroxyl can participate in the polymerization reaction of polyurethane as a crosslinking agent.
Hydroxylation of vegetable oils has been widely reported, such as epoxy ring-opening [25], transesterification [26], hydroformylation, ozonization [27], thiol-ene photo-click reaction, etc. [28]. Among these methods, thiol-ene photo-click reaction has become an effective method to prepare vegetable oil-based polyols due to its advantages of one-step reaction, short time, high conversion rate and the introduction of high active primary hydroxyl group [29]. The higher iodine value provides the basis for the addition of mercaptoethanol to its molecules and also provides the primary hydroxyl group to prepare polyols with high hydroxyl value as cross-linking agent [30]. Therefore, the sapium sebiferum oil-based crosslinking agent can be prepared by adding hydroxyl group to SO by mercaptoethanol.
In this paper, we prepared a novel crosslinking agent based on sapium sebiferum oil and introduced it into castor oil-based polyurethane to increase its crosslinking and improve its performance. We used sapium sebiferum oil and mercaptoethanol to prepare sapium sebiferum oil-based polyol by thiol-ene photo-click reaction. The molecular structure and hydroxyl values of these polyhydric crosslinking agents were characterized. Then, we introduced the sapium sebiferum oil-based polyol into castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane to prepare modified castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane (CWPU-SOP). The particle size and the chemical structure of the emulsion were tested, and anti-graffiti properties, water contact angle and mechanical properties of the films were measured under different mass ratio of SOP to CO.